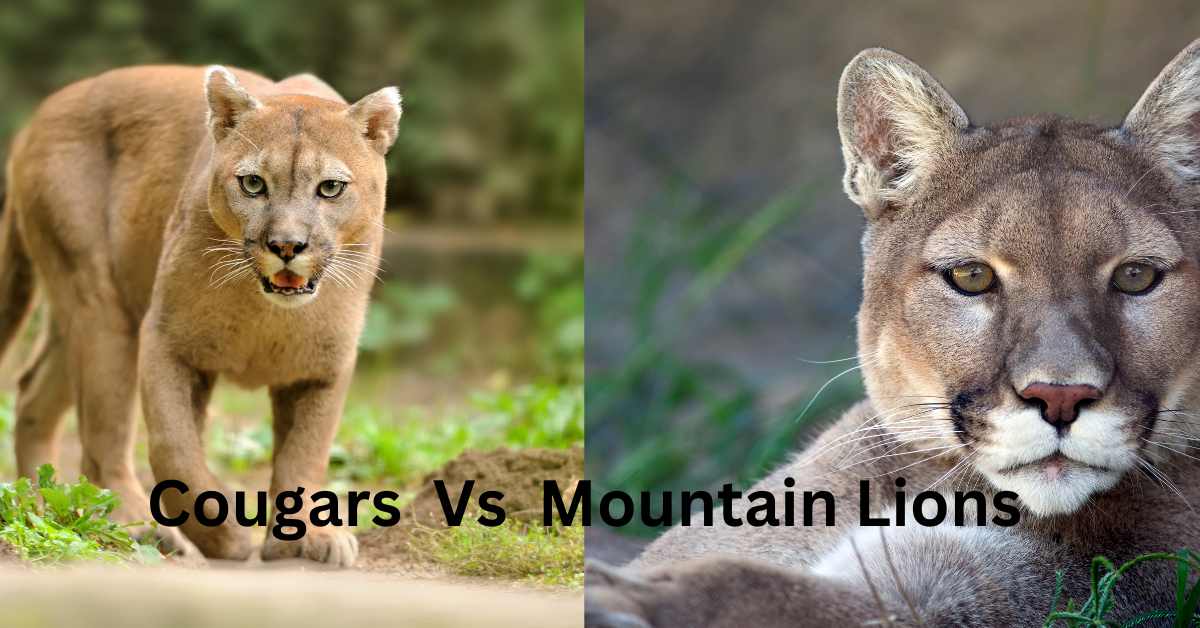
Also known as ‘the cat of many names’, cougars and mountain lions are the same animal. They are recognised by different names across various parts of the world, which leads to the confusion. However, based upon their geographical location, climate and diet type, a few differences between cougars and mountain lions is possible.
Below we will be discussing these very differences in detail. So let’s dive in without any further ado.
Are Cougars and Mountain Lions the same?
Belonging to the Felidae family, this majestic animal has many names. From being recognised as the Cougars in South America to panthers and mountain lions in the Northern side, this big cat also goes by the names of painters, pumas, catamounts, etc.
And although they belong to the same family of animals, certain subtle variations cause their physical forms to change, thereby creating even more confusion amongst the public.
The same is also claimed by Charlie Jasper, founder of C&C Security Consultants, whose work involves preventing these predators from accessing his client’s private property spread within the Los Angeles wilderness. He states that, ‘There are no significant differences between cougars and mountain lions other than their vernacular taxonomy”.
So, Are there any differences between Cougars and Mountain Lions?
Habitat and Geographical Distribution
Starting with the very first difference, mountain lions and cougars have variable natural habitat preference. While they are the same animal, their preference according to the climatic conditions of the area differ a lot.
For instance, mountain lions have a relatively larger range of habitat and distribution spreading all across North and Central America, contrary to Cougars whose population are more laid out towards lowland areas, forests and mountain deserts of South America.
Physical Appearance
When it comes to their bodies, there is only one major difference between cougars and mountain lions, that is their fur texture and thickness. As their name suggests mountain lions stay in colder areas, including hill tops and mountains. Therefore, to protect their skin from the extreme cold, these animals have evolved to have much thicker fur than their other siblings that reside in relatively less chilly areas.
On the other hand, cougars have a coarse, short textured coat that keeps them well ventilated and ready for tropical climates.
Diet
Based upon the terrain they are residing in, mountain lions and cougars have variable diet preferences. Although they are never picky and can do well with all kinds of animals, the availability of the local species is what causes the difference between cougars and mountain lions and their diet.
So, based upon their habitat, mountain lions prey on deers and mountain sheeps. Whereas on the other side, cougars love hunting llama, vicuna, guanaco, capybara, and alpacas.
Coat Color and Texture
Like discussed earlier, mountain lions have furry coat arrangements to protect them from the harsh cold climates. Moreover, they are generally found having silvery fur that helps them camouflage better in the thick sheets of snow when hunting.
But cougars exhibit both orange-brown, yellowish-brown, and reddish colorations. This basically relies on the type of climate they are subjected to, with reddish colored coats mostly visible towards warm areas.
Below we have compiled all these data into an easy-to-follow form.
| FACTORS | COUGARS | MOUNTAIN LIONS |
| Family | Felidae, Big Cats | Felidae, Big Cats |
| Habitat Range | South America | North and Central America |
| Physical Difference | Slightly smaller | Slightly larger |
| Climate Preference | Warmer area, deserts and low lands | Colder areas, top of mountains and hills |
| Coat Texture | Coarse, short fur | Furry and thick with longer furs |
| Diet Preference | Alpacas, llamas, capybara, vicuna, guanaco | Deers and Mountain Sheep |
| Coat Colour | Tawny or reddish coloured fur, with lighter underbelly | Silver coloured fur |
| Attack on Humans | Relatively high | Considerably low |
Final Thoughts
So, ultimately, both cougars and mountain lions are the same animal. However, a few differences between cougars and mountain lions pop up when we look at their natural habitat, diet, and physical forms which could be confusing initially. Therefore, an easier way to determine if your region may have cougars or mountain lions is to look carefully at your annual climatic conditions.
For interesting updates like these, subscribe to our mailing list today at differencio.com.