Introduction
Lung cancer is one of the significant causes of cancer-related deaths and accounts for nearly 25% of cases worldwide. 70% of lung cancer conditions result from smoking, with secondhand smoke and air pollution less common causes. Owing to delayed diagnosis, the five-year survival rate of carcinoma is often only 15%, and yearly almost 130,180 people end up losing their lives. Along with the delayed onset of symptoms, delayed diagnosis because of similar symptoms with other systemic complications is one of the chief reasons it takes longer to diagnose lung cancer. Lung cancer and Mesothelioma are two different carcinomas confused because of similar symptoms.
Knowing them briefly will help clear several misconceptions regarding their causes and treatment options.
What is Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is an asbestos exposure-related cancer that derives its name from its origin in the mesothelial layer, the thin layer of tissue covering the internal organs. Exposure to asbestos in the form of working with asbestos products, living with workers involved in the production of asbestos, or working in buildings containing asbestos is the chief cause of Mesothelioma.
Factories, constructions, mining, shipbuilding, and manufacturing industries involving asbestos are some of the chief exposure areas leading to mesothelioma conditions. In addition, disturbance of asbestos-containing materials through factors involving degradation of building materials or through their disturbance as a result of construction or repair are some other triggers for Mesothelioma conditions. Rarely environmental asbestos exposure can occur due to the release of naturally occurring asbestos in the air through human activity or weathering conditions.
All things said, asbestos exposure accounts for nearly 80% of mesothelioma cases, with the risk of cancer increasing with exposure. Apart from asbestos exposure, family history of Mesothelioma and prior history of radiation therapy for lung cancer are other risk factors that can trigger the phenomenon. The latency period of Mesothelioma can range from 13-70 years, depending on the source of exposure in patients.
| Type of Mesothelioma | Occurrence | incidence | symptoms | Life expectancy |
| Peritoneal Mesothelioma | Abdominal regions | 10-20% | Abdominal pain, bloating, bowel changes | Five years or more after diagnosis |
| Pleural Mesothelioma | lungs | 70-75% | Shortness of breath, chest pain, fever, fatigue | Three years or more in stage 1.12 months at Stage IV |
| Pericardial Mesothelioma | heart | 1% | Irregular heartbeat, chest pain, cough | Six weeks -15 months |
| Testicular Mesothelioma | testes | 1% | Scrotal swelling, painless testicular lumps | < 2 years after diagnosis |
Chest x-rays, CT Scans, Echocardiograms, PETs, and MRIs are some imaging tests used to diagnose the issue. Blood tests and tissue sampling with biopsies are other diagnostic methods. Once the diagnosis has been confirmed, Surgery, Chemotherapy, and Radiation Therapy with Palliative measures are among the most common treatment methods.
What is Lung Cancer
Lung cancer or lung carcinoma is a malignant lung tumor that occurs due to uncontrolled cell growth within the tissues of the lungs. The human lungs consist of
Lobes – rounded divisions of the lungs filled with sponge-like tissues
Trachea – the tube connecting the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs
Bronchi – airways in the lower respiratory tract conducting air inside the lungs
Bronchioles – tubes in the lungs that branch off from the larger bronchi and carry air into the alveoli
Alveoli – air sacs at the end of bronchioles where the actual exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place
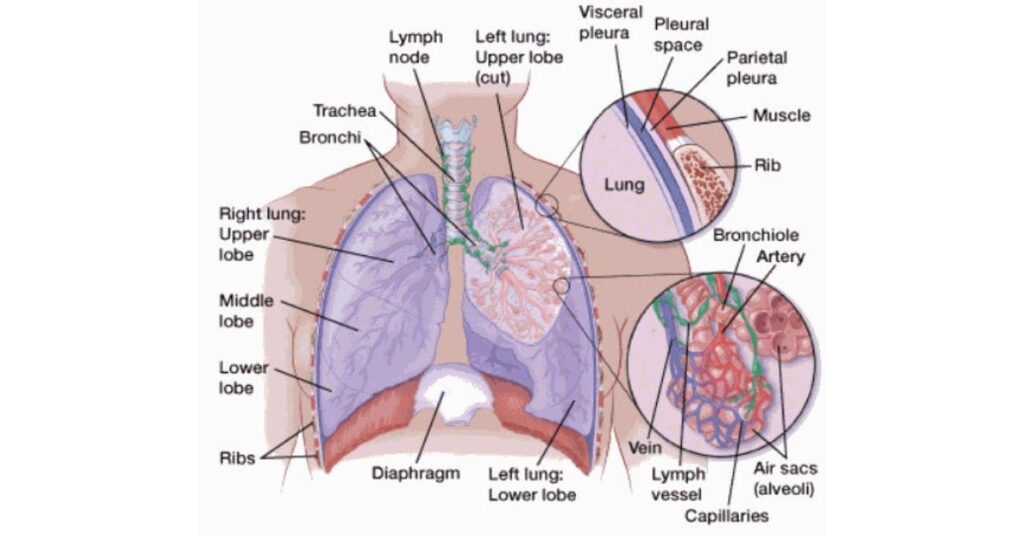
Lung cancers start in the cells of the bronchi, bronchioles, or alveoli of the lungs and symptomize in the form of coughing, shortness of breath, and wheezing before invading the lymph nodes and traveling to other parts of the body. The liver, adrenal glands, bones, and brain are some common metastasis locations where secondary tumors are formed with accompanying complications.
Bone pain, swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck or above the collarbones, and yellowing of the skin and eyes with nervous system changes like seizures or balance problems are some of the chief symptoms of metastasis of lung cancer.
| Types of lung cancer | Incidence | Growth Rate | Stages |
| NSCLC | 80%-85% | slower | Hidden stage up to Stage IV |
| SCLC | 10%-15% | faster | Limited stage and extensive stage |
| Lung tumors | Less than 5% | slower | – |
Imaging tests, Sputum cytology, and tissue samples are some of the most common diagnostic methods of lung cancer, in addition to CTs, MRIs, and bone scans that help determine whether or not cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Once diagnosed, surgeries, chemotherapies, radiation therapies, and targeted drug therapies are some of the most common treatment measures advised by oncologists.
Difference between Mesothelioma and Lung cancer
| Characteristics | Mesothelioma | Lung Cancer |
| Cause | Ingesting or inhaling microscopic asbestos fibers | Genetics, smoking history, air pollution, radiation, HIV, exposure to asbestos fibers |
| Latency period | 20-60 years | 10-30 years |
| Occurrence site in the system | Around the lungs | Within the lungs |
| Growth pattern | It starts as nodular growth that, in time, fuse together | Defined boundaries in individual masses |
| Area of occurrence | The lining of the Lungs, heart, abdomen, testes | Within lungs |
| Symptoms | Observed in early stages | Observed in late stages |
| Chief symptoms | Chest pain, shortness of breath | Worsening cough, coughing up blood, bronchitis, pneumonia |
| Pleural effusion occurence | 90% | 40% |
| Pleural thickening | Common occurrence | May or may not occur |
| Immunotherapy | Not applicable | Applicable |
| Survival rate a year after diagnosis | 39% | 42% |
| The survival rate after five years | 12% | 25% |
| Smoking | Indirect reason for Mesothelioma | The primary reason for lung cancer |
Conclusion
Getting medical help in the early stages of the issues can help diagnose and differentiate between lung cancer and Mesothelioma. Equally important are preventive care methods such as following a healthy lifestyle and wearing safety gear in asbestos-prone regions. Most importantly, getting periodic health checkups can help in undetected cancerous growth and enable you to get early help.