What is Monovalent Covid Booster?
A monovalent covid booster is a vaccine with one strain of the virus. A vaccine is a specially prepared antigen administered to a person to provide immunity designed to trigger an immune response within the body and make it stronger for fighting the virus. Boosters are additional vaccinations provided after the protection offered by the original vaccines starts wearing out in time. Monovalent Covid boosters are the early Covid boosters created using the original strain of Covid-19.
Based on the mechanism of action, Covid boosters are either.
- Messenger RNA Vaccine
- Vector Vaccines
- Protein Subunit Vaccines
Monovalent Covid Boosters were designed on all three mechanisms; Pfizer and Moderna are monovalent mRNA vaccines, Janssen/ Johnson and Johnson is a mono Covid vector vaccine, and Novavax Covid 19 is a protein subunit vaccine.
While Monovalent covid boosters were adequate for the early stains of Covid-19, the virus variants developed a resistance to them and reduced their effectiveness. Because of this, researchers came up with modified Covid vaccinations or bivalent covid boosters.
What is a Bivalent Covid Booster?
A bivalent or multivalent Covid booster is an additional Covid booster that contains multiple virus strains. It has been designed as an additional booster that can be taken after the monovalent covid booster.
It is important to understand that Covid-19 tends to form variants that differ from the original virus regarding genetic mutations. This does not change the overall pattern of infection. But because the vaccines are programmed keeping in mind the original virus structure, they lose their effectiveness when exposed to the variants.
Bivalent Covid booster works against multiple Covid variants like Omicron BA.2, BA.4-5, ad some older Covid strains.
Here are some chief differences between monovalent and bivalent Covid boosters.
Chief areas of difference
Virus strains
Monovalent covid boosters are effective for earlier Covid-19 ancestral strains and early variants like the Delta Strain.
Bivalent covid boosters are effective for newer Covid strains like Omicron and its sublineages like BA.2, BA.4, and BA.5.
Effectiveness
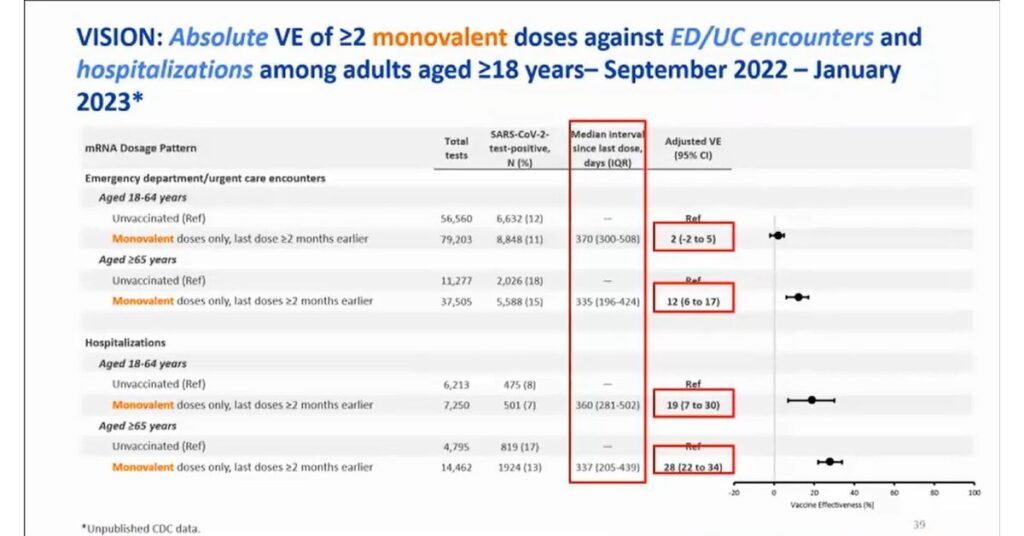
Bivalent covid boosters have an increased effectiveness than monovalent ones. In a study conducted on 300000 participants, researchers found that bivalent boosters had a 62% effectiveness compared to 25% in monovalent boosters.
Age groups
People 12 years of age or older can access monovalent covid boosters.
Children six months to four years and older can access bivalent covid boosters as per the advice of their healthcare provider.
Hospitalization
Monovalent boosters are approximately 25% effective in preventing hospitalization.
Studies have shown that bivalent boosters reduce hospitalization by 57% in people who haven’t been vaccinated and reduce the hospitalization rate to 45% in people vaccinated 11 months earlier.
In total, the bivalent boosters were 37% more effective in preventing hospitalization and death.
Longevity of dose
Clinical data have shown that monovalent Covid boosters are effective for approximately six months, and after that, their effectiveness starts waning.
Bivalent boosters are effective for a slightly more extended period of a year.
Studies determining the effectiveness of booster shots among 883 participants in Wisconsin aged five years and older showed that the monovalent covid booster was 74% effective against Omicron infection for the first three months, after which its protection waned to 42% from 3-6 months and 36% after six months.
Virus Severity
Monovalent boosters lose their effectiveness in Severe Covid conditions.
Bivalent boosters are 37% more effective than monovalent boosters in reducing the risk of Covid infection.
When to get
You must wait at least six months after the covid vaccine to get the monovalent booster.
The correct time to take a bivalent covid booster depends on age and previous vaccination status. E.g., People administered monovalent boosters can take a bivalent booster after approximately eight weeks of the initial booster. The general practitioner determines your dose eligibility in pediatric cases and older adults above 65 years.
Immunocompromised people
Immunocompromised individuals six months or older that have previously received only monovalent covid boosters/ vaccines are advised to receive 1-2 bivalent booster shooters depending on their age and vaccine product.
Immunocompromised people that have received a bivalent covid vaccine booster can receive one or an additional bivalent booster shot.
Eligibility
People aged five to 11 years are recommended to get the original (monovalent) booster.
People 12 years and older should receive one updated bivalent booster.
The time interval between two boosters
There should be at least two months of the time interval between monovalent booster shots.
There should be a gap of 8 weeks between the first two bivalent covid boosters and 28 days between the third bivalent booster shot.
Side effects
Monovalent covid booster – Pain or tenderness, swelling of lymph nodes in the arm where you were given the injection, tiredness, headache, nausea, muscle or joint pain
Bivalent covid booster – itching, redness, fatigue
Tabular form
| Characteristics | Monovalent Covid Booster | Bivalent Covid Booster |
| Composition | One strain of virus | Two strains of the virus |
| Designed For | Early strains of Covid Strains | Later Covid strains |
| Effectiveness | 25% | 62% |
| Age Group | 12 years or older of age | Six months or older of age |
| Preventing Hospitalization | 25% effective in preventing hospitalization | 37% effective in preventing hospitalization |
| How long do they last | Approximately six months | Approximately one year |
| In severe Covid conditions | Less effective | More effective |
| When to get | Six months after Covid vaccine | As per the physician’s guidance |
| In Immunocompromised people | Need a bivalent shot if they have previously received a monovalent shot | Need an additional bivalent dose after the bivalent doses |
| Eligibility | 5-11 years | 12 months or older |
| Time Interval | Two months | Eight weeks |
| Side Effects | pain, swelling, tiredness | Redness, itching, fatigue |
| Example | Novavax | Moderna |
Reference:
- www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/how-do-vaccines-work#:~:text=Vaccines%20contain%20weakened%20or%20inactive,rather%20than%20the%20antigen%20itself.
- doh.wa.gov/sites/default/files/2022-12/825082-COVID19VaccinesMonovalentVSBivalent.pdf
- www.news-medical.net/news/20230322/Monovalent-vs-bivalent-vaccines-e28093-Which-is-more-effective-against-SARS-CoV-2.aspx
- covid19.nih.gov/news-and-stories/bivalent-boosters-offer-better-protection-against-omicron#:~:text=The%20research%20team%20found%20that,in%20preventing%20hospitalization%20and%20death.
- www.ama-assn.org/delivering-care/population-care/covid-19-bivalent-boosters-young-children-what-parents-must-know